- Posts about parallels written by fancypearlsmith. After an abundant amount of research and multiple inquiries to my “geek friends,” I believe that I have finally created a decent comparison chart that outlines pros and cons of each product that is in the running to run Windows software on Mac.
- In computing, a group of parallel arrays (also known as structure of arrays or SoA) is a form of implicit data structure that uses multiple arrays to represent a singular array of records. It keeps a separate, homogeneous data array for each field of the record, each having the same number of elements.
- Parallels Desktop 12 doesn't have the eye-catching features of last year's edition, but improved performance, time-saving options, and regular updates should help to maintain its lead over.
- Dec 19, 2019 Parallel Play in Early Childhood – Pros and Cons By Chris Drew, PhD / December 19, 2019 April 29, 2021 Parallel play is a type of play-based learning that involves students playing alongside each other but not in collaboration.
There are many reasons why Windows simulators are popular even though macOS is already a great platform on its own. It could be because you want to enjoy features that are only available on Windows or you need to run Windows-based apps for school or work. It could also be that you’re simply more familiar with Windows and you’re more comfortable using it than your Mac.
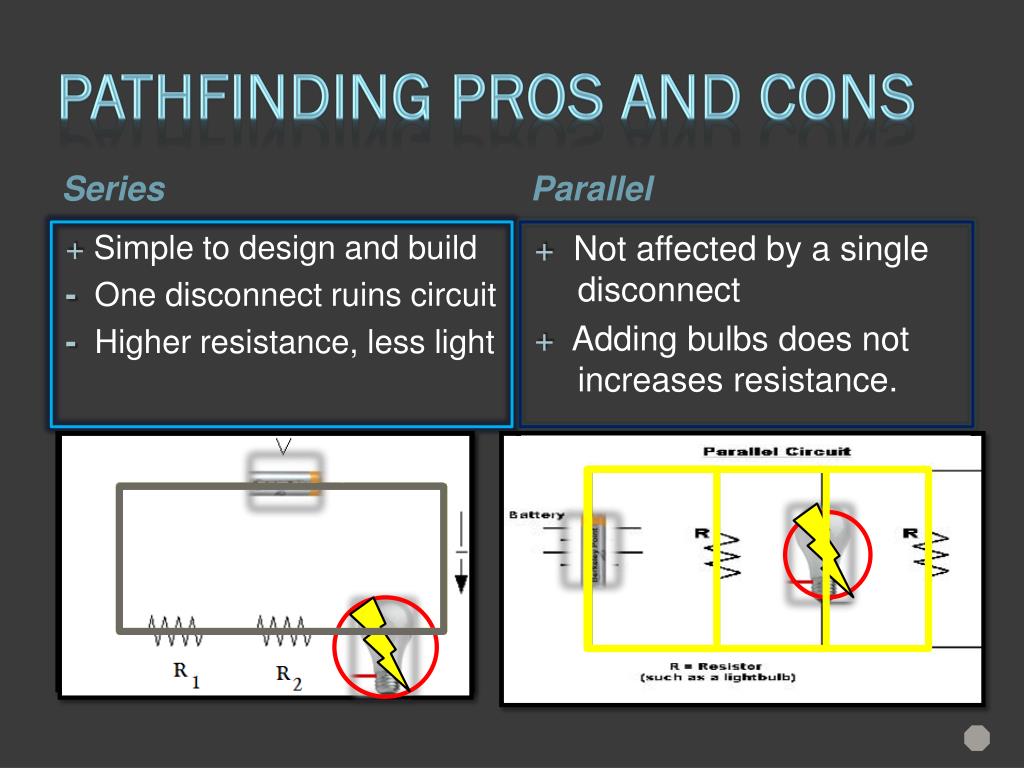
Parallels Desktop Pros and Cons of Boot Camp, Boot Camp-Based VM, and Parallels Desktop Virtual Machine.See disk space information below.While Boot Camp provides performance benefits to high-end graphics-intensive applications, most Office workloads don't benefit from using Boot Camp.
Whatever your reason is, running Windows on Macs has become a lot easier using simulators. One of the popular virtual platforms that you can use to run a different operating system on macOS is Parallels Desktop. This virtualization platform may not be the only software that allows Mac users to run Windows apps, but expert users prefer the speed, efficiency, and ease of use provided by Parallels Desktop.
Parallels Desktop is a great way of running Windows apps on Mac, especially for regular users. Aside from Windows, you can also run other operating systems and other OS-based apps on this virtualization platform.
What is Parallels Desktop 13?
Parallels has released several versions of the Parallels Desktop software already, with each version making it easier to run Windows OS and other operating systems, including older versions of macOS and Mac OSX. But one of the best versions released of this virtualization platform is the Parallels Desktop 13. It is the first version of the software that allows Mac users to launch Windows apps and provide some control using the MacBook Pro Touch Bar. With this version, you can enable the Touch Bar to display various tools and features from the virtual machines. Aside from the Touch Bar, users can also use the new People Bar and Picture-in-Picture features on Windows 10.
Imvu mac beta. Pro Tip: Run a dedicated PC optimization tool to get rid of incorrect settings, junk files, harmful apps, and security threats that can cause system issues or slow performance.
Free Scan for PC IssuesSpecial offer. About Outbyte, uninstall instructions, EULA, Privacy Policy.
Aside from the Parallels Desktop 13 for Mac, Parallels Desktop for Mac Pro Edition and Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition are also available for download.
To use Parallels Desktop 13, these are the hardware requirements you need to consider:
- At least late 2012 Mac or later
- 4 GB of memory, 8 GB is recommended
- At least 850 MB of disk space on the boot volume for the Parallels Desktop installation.
- Additional disk space for virtual machines, depending on the operating system you want to install
- If you have an SSD drive, that would be better
- An internet connection for product activation and other features
Aside from the hardware requirements, you also need to have the necessary software requirements, which include:
- macOS High Sierra 12.13
- macOS Sierra 10.12.5 or later
- OS X El Capitan 10.11.6 or later
- OS X Yosemite 10.10.5 or later
Here are the 32-bit operating systems you can run on your Parallels Desktop:
- Windows 10
- Windows 10 Creators Update
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 8
- Windows Server 2012 R2, and SP0
- Windows 7 SP1, and SP0
- Windows Server 2008 R2, SP2, SP1, and SP0
- Windows Vista Home, Business, Ultimate, Enterprise SP2, SP1, and SP0
- Windows Server 2003 R2, SP2, SP1, and SP0
- Windows XP Professional SP3, SP2, SP1, and SP0
- Windows XP Home SP3, SP2, SP1, and SP0
- Windows 2000 Professional SP4
- Windows 2000 Server SP4
- Windows NT 4.0 Server SP6
- Windows NT 4.0 Workstation SP6
- Windows ME
- Windows 98 SE
- Windows 95
- Windows 3.11
- MS-DOS 6.22
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, 6, and 5
- Fedora Linux 26, 25, 24, 23, 22, 21, 20, and 19
- Ubuntu 18.04, 17.04, 16.10, 16.04 LTS, 15.10, 15.04, 14.10, 14.04 LTS, 13.10, 13.04, 12.10, 12.04 LTS, 11.10, 11.04, 10.10, and 10.04 LTS
- CentOS Linux 7, 6, and 5
- Debian Linux 8, 7, 6, and 5
- Suse Linux Enterprise 12, 11 SP3, and 11 SP2
- openSUSE Linux 13.2, 13.1, and 12.3
- Linux Mint 18, 17, 16, and 13
- Kali Linux 2018.1, and 2017.1
- Zorin OS 12.1
- elementary OS 0.4
- Manjaro Linux 17.0.1
- Mageia 5, 4.1, and 3
- Solaris 11.3, 11, and 10
- OpenBSD 6
- FreeBSD 11, 10, 10, 9, and 8
- OS/2 Warp 4.5 and 4
- eComStation 2 and 1.2
- Mac OS X Leopard Server 10.5.x
- Mac OS X Snow Leopard Server 10.6.x
- Android OS downloaded by the Installation Assistant)
Here are the 64-bit operating systems you can run on Parallels Desktop:

- Windows 10
- Windows 10 Creators Update
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 8
- Windows Server 2012 R2 and SP0
- Windows 7 SP1 and SP0
- Windows Server 2008 R2, SP2, SP1, and SP0
- Windows Vista Home, Business, Ultimate, Enterprise SP0, SP1, and SP2
- Windows Server 2003 R2, SP2, SP1, and SP0
- Windows XP Professional SP2
- boot2docker
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, 6, and 5
- Fedora Linux 26, 25, 24, 23, 22, 21, 20, and 19
- Ubuntu 17.04, 16.10, 16.04 LTS, 15.10, 15.04, 14.10, 14.04 LTS, 13.10, 13.04, 12.10, 12.04 LTS, 11.10, 11.04, 10.10, and 10.04 LTS
- CentOS Linux 7, 6, and 5
- Debian Linux 8.3, 7, 6, and 5
- Suse Linux Enterprise Server 12, 11 SP3, and 11 SP2
- openSUSE Linux 13.2, 13.1, and 12.3
- Linux Mint 18, 17, 16, and 13
- Kali Linux 2017.1
- Zorin OS 12.1
- elementary OS 0.4
- Manjaro Linux 17.0.1
- Mageia 5, 4.1, and 3
- OpenVZ 7
- Solaris 11.3, 11, and 10
- OpenBSD 6
- FreeBSD 11, 10, 10, 9, and 8
- macOS Sierra 10.12.x
- OS X El Capitan 10.11.x
- OS X Yosemite 10.10.x
- OS X Mavericks 10.9.x
- OS X Mountain Lion 10.8.x
- OS X Lion 10.7.x
- OS X Lion Server 10.7.x
- Mac OS X Snow Leopard Server 10.6.x
- Mac OS X Leopard Server 10.5.x
Parallels Desktop 13 Pros and Cons
One of the main features of Parallels Desktop 13 is that it brings Windows apps to the Mac’s Touch Bar. It supports Mac Touch Bar integration for Microsoft Word, Outlook, Excel, and PowerPoint, and browsers, such as, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, and Opera. When you open the Windows Start Menu or Desktop, you can immediately see the Taskbar pinned elements, along with Task View, Cortana, and settings in the Touch Bar. Most of the Windows programs that run in Parallels Desktop can be quickly customized with preset Touch Bar actions if the built-in set of functional keys is not sufficient.
Aside from enhancing existing Mac features, Parallels Desktop is also able to build on Windows tools as well. Parallels Desktop 13 integrates the Windows 10 Insider Preview’s People Bar, a Windows 10 feature that allows users to pin contacts to the Taskbar. Although Windows you can only pin up to three People Bar contacts, the Dock on macOS doesn’t limit favorite contacts. It even displays larger photos for easy viewing.
The new Parallels Desktop 13 also includes Picture-in-Picture (PiP) View, a Windows feature that creates windows of other active virtual machines (VMs). These VMs are always visible on top, even when an application is in Full Screen mode. With this, you can easily monitor and work with multiple operating systems and apps simultaneously on one screen. It also allows you to watch a video while switching between macOS Spaces and other programs. Aside from PiP View, here are other popular Parallels Desktop customization settings you should try:
- Coherence – Windows is invisible while using Windows apps on a Mac
- Full Screen mode – Enjoy your windows and apps on fullscreen
- Window mode – Windows in a window in macOS
The Parallels Desktop for Mac Business Edition also features a customer-inspired Single Application mode. This mode lets IT admins deliver, lock, and secure invisible Windows virtual machines with specific applications to the Dock. This makes it easy for users to discover and use Windows apps just like Mac apps. Parallel Desktop 13 also provides a couple of visual and display improvements for better transitions and improved scaling resolution.
There are also more than 30 easy-to-use utilities for Mac and Windows included in Parallels Desktop 13. Some of the more popular utilities include:
- Clean Drive – This tool allows users to easily free up disk space.
- Presentation Mode – This mode prevents embarrassing notifications, accidental display of personal files, and screensaver lockout delays when doing a presentation.
- Download Video – Download videos from YouTube, Facebook, and other streaming websites in just one click.
- Find Duplicates – This allows you to easily search any drive or folder to filter identical files, even with different names, and free up your storage space.
- Record Screen – Record a video of your entire screen, an active window, or a selected area with audio.
Parallels Desktop 13 Pricing
Parallels Desktop 13 is available for new subscribers and upgraders from the 11th and 12th version. If you have an existing Parallels Desktop software, you can upgrade to the Parallels Desktop 13 version using this link.
For new subscribers, you can get your copy of Parallels Desktop 13 from the developers’ website or at online stores around the world. Here are the prices for the various Parallels Desktop 13 packages:
- Parallels Desktop 13 for Mac – $79.99
- Upgrades for existing Parallels Desktop 11 and 12 for Mac – $49.99
- Parallels Desktop Pro Edition subscription – $49.99 per year
- Parallels Desktop for Mac Pro Edition – $99
- Parallels Desktop for Business – $99
Parallels Desktop 13 has a free 14-day full-featured trial period so you can see how the app works and try out the different features.
How to Use Parallels Desktop 13
To use Parallels Desktop 13, you need to download the software from the website. You can directly buy the app or download a trial version. Once the installer has been downloaded, click on the file to install it on your computer.
After the installation has been completed, you’ll find Parallels Desktop in your Menu Bar at the top of the screen. Click on the Parallels icon, which is two red vertical lines, to launch the software. This menu allows you to choose your view, manage your devices, enter a different mode, and other actions.
There are several ways to open a Windows app. You can choose to launch the apps from the Windows Applications folder in the Dock, the Windows Start menu, the Dock, via Spotlight searching, or using Launchpad. You can identify Windows apps easily by the Parallels Desktop symbol found in the lower-right corner of the app’s icon. You can also install new apps from the Windows Store, from the internet, or via CD/DVD.
If you’re running into errors and your system is suspiciously slow, your computer needs some maintenance work. Download Outbyte PC Repair for Windows or Outbyte Antivirus for Windows to resolve common computer performance issues.Fix computer troubles by downloading the compatible tool for your device.In computing, a group of parallel arrays (also known as structure of arrays or SoA) is a form of implicit data structure that uses multiple arrays to represent a singular array of records. It keeps a separate, homogeneous data array for each field of the record, each having the same number of elements. Then, objects located at the same index in each array are implicitly the fields of a single record. Pointers from one object to another are replaced by array indices. This contrasts with the normal approach of storing all fields of each record together in memory (also known as array of structures or AoS). For example, one might declare an array of 100 names, each a string, and 100 ages, each an integer, associating each name with the age that has the same index.
Examples[edit]
An example in C using parallel arrays:
in Perl (using a hash of arrays to hold references to each array):
Pros And Cons Meaning
First person shooter games on mac. Or, in Python:
Pros and cons[edit]
Parallel arrays have a number of practical advantages over the normal approach:
Parallels Pros And Cons 2020
- They can save a substantial amount of space in some cases by avoiding alignment issues. For example, some architectures work best if 4-byte integers are always stored beginning at memory locations that are multiple of 4. If the previous field was a single byte, 3 bytes might be wasted. Many modern compilers can automatically avoid such problems, though in the past some programmers would explicitly declare fields in order of decreasing alignment restrictions.
- If the number of items is small, array indices can occupy significantly less space than full pointers, particularly on some architectures.
- Sequentially examining a single field of each record in the array is very fast on modern machines, since this amounts to a linear traversal of a single array, exhibiting ideal locality of reference and cache behaviour.
- They may allow efficient processing with SIMD instructions in certain instruction set architectures
Several of these advantage depend strongly on the particular programming language and implementation in use.
However, parallel arrays also have several strong disadvantages, which serves to explain why they are not generally preferred:
- They have significantly worse locality of reference when visiting the records non-sequentially and examining multiple fields of each record, because the various arrays may be stored arbitrarily far apart.
- They obscure the relationship between fields of a single record (e.g. no type information relates the index between them, an index may be used erroneously).
- They have little direct language support (the language and its syntax typically express no relationship between the arrays in the parallel array, and cannot catch errors).
- Since the bundle of fields is not a 'thing', passing it around it tedious and error-prone. For example, rather than calling a function to do something to one record (or structure or object), the function must take the fields as separate arguments. When a new field is added or changed, many parameter lists must change, where passing objects as whole would avoid such changes entirely.
- They are expensive to grow or shrink, since each of several arrays must be reallocated. Multi-level arrays can ameliorate this problem, but impacts performance due to the additional indirection needed to find the desired elements.
- Perhaps worst of all, they greatly raise the possibility of errors. Any insertion, deletion, or move must always be applied consistently to all of the arrays, or the arrays will no longer be synchronized with each other, leading to bizarre outcomes.
The bad locality of reference can be alleviated in some cases: if a structure can be divided into groups of fields that are generally accessed together, an array can be constructed for each group, and its elements are records containing only these subsets of the larger structure's fields. (see data oriented design). This is a valuable way of speeding up access to very large structures with many members, while keeping the portions of the structure tied together. An alternative to tying them together using array indexes is to use references to tie the portions together, but this can be less efficient in time and space.
Another alternative is to use a single array, where each entry is a record structure. Many language provide a way to declare actual records, and arrays of them. In other languages it may be feasible to simulate this by declaring an array of n*m size, where m is the size of all the fields together, packing the fields into what is effectively a record, even though the particular language lacks direct support for records. Some compiler optimizations, particularly for vector processors, are able to perform this transformation automatically when arrays of structures are created in the program.[citation needed]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. Introduction to Algorithms, Second Edition. MIT Press and McGraw-Hill, 2001. ISBN0-262-03293-7. Page 209 of section 10.3: Implementing pointers and objects.
- Skeet, Jon (3 June 2014). 'Anti-pattern: parallel collections'. Retrieved 28 October 2014.